Determining product price is not a one-time task; it is a continuous strategic process. It requires balancing internal costs, market position, perceived customer value, and overarching business goals. For B2B decision-makers, mastering this process is fundamental to protecting margins and ensuring sustainable growth.
Why Outdated Pricing Models Are a Commercial Risk
In today's B2B environment, relying on outdated pricing models is a direct threat to profitability. The traditional cost-plus method—calculating total costs and adding a standard markup—creates a significant blind spot. It ignores crucial external factors like real-time market dynamics, competitor actions, and customer value perception.
This simplistic approach exposes your business to immediate and significant risks:
- Margin Erosion: Pricing too high relative to the market can lead to lost sales and a decline in market share.
- Revenue Leakage: Pricing too low without a clear understanding of market value means sacrificing profit on every transaction.
- Brand Damage: Inconsistent pricing across different sales channels or marketplaces confuses customers, erodes trust, and undermines MAP/RRP (Minimum Advertised Price/Recommended Retail Price) enforcement.
A modern pricing strategy must be built on real-time data and a comprehensive understanding of several key components.
The Pillars of a Modern Pricing Framework
A practical and effective framework for determining product price rests on four pillars. Each provides a layer of insight that helps you identify the optimal price point.
First is a thorough cost analysis. This includes not only the cost of goods but every expense required to deliver the product to the customer. This figure establishes your absolute pricing floor—the point below which a sale becomes unprofitable.
Second is real-time market intelligence. Pricing cannot be done in a vacuum. It is essential to know how competitors are pricing similar products, their current stock levels, and their promotional activities. For instance, a manufacturer needs to monitor dozens of online resellers to ensure MAP compliance, a task that is impossible to perform manually at scale.
Third is the customer's perception of value. What specific problem does your product solve? What is that solution worth to your customer's business? This shifts the focus from your internal costs to their tangible gains.
Finally, pricing must align with your strategic business goals. Are you aiming to penetrate a new market, maximize short-term profits, or build long-term customer loyalty? Your pricing will be a direct reflection of these objectives.
Effective pricing is not a static decision but an ongoing, data-driven process. The businesses that succeed are those that can continuously adjust their strategy based on market signals. This is where automated price monitoring tools like Market Edge become useful.
Calculate Your True Costs to Establish a Solid Pricing Floor
Every robust pricing strategy begins with a precise understanding of your costs. Before considering profit margins or competitor actions, you must establish your pricing floor. This is your absolute break-even point—the number below which every sale results in a loss.
A common error is to define "cost" as merely the supplier price. This narrow view ignores numerous other expenses that accumulate before a product reaches the customer. A comprehensive cost analysis is the foundation of your pricing plan; without it, you are operating on assumptions.
Go Beyond the Supplier Invoice: Calculate Your Total Landed Cost
To set a reliable pricing floor, you must calculate the total landed cost for each product. This figure represents the sum of all expenses incurred to bring an item from the supplier to your warehouse, ready for sale.
A proper landed cost calculation includes:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct price paid to your supplier or the cost to manufacture the product.
- Inbound Logistics: All costs associated with moving the product, including freight, shipping insurance, and handling fees.
- Import-Related Fees: For importers, this includes tariffs, customs duties, brokerage fees, and port charges. These can fluctuate with trade policies and require ongoing monitoring.
- Warehousing and Fulfillment: The costs to store, pick, pack, and prepare products for shipment.
- Payment Processing: The fees charged by payment gateways on each transaction.
Only by aggregating these components can you establish an accurate cost basis for your products.
This diagram illustrates how the elements of a pricing strategy interrelate, with costs forming the essential foundation.
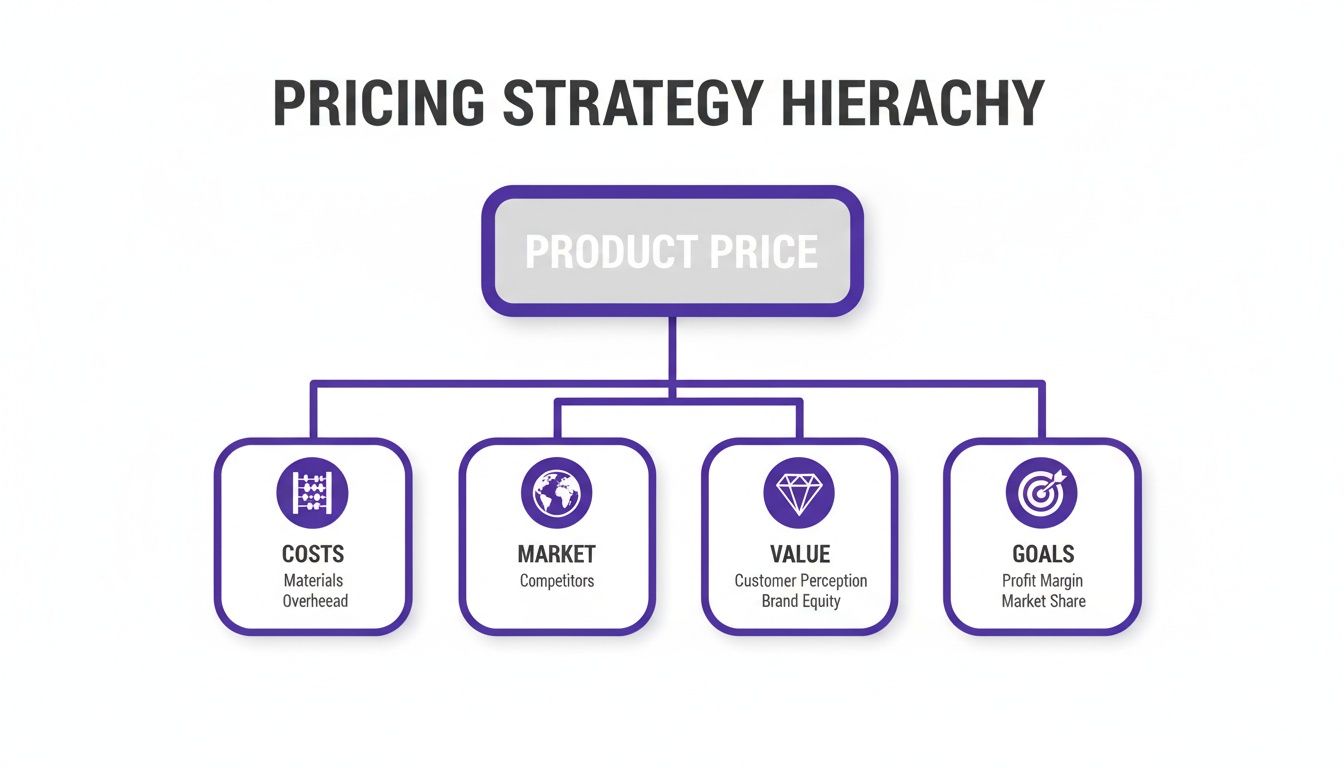
While market demand and business goals shape the final price, internal costs set the non-negotiable minimum required to remain solvent.
Mini Use Case: An Industrial Distributor
Consider an industrial parts distributor importing a specialized valve. The common approach is cost-plus pricing, which involves adding a markup to the supplier's price. (We explore this method in our guide to cost-plus pricing examples.)
However, a true cost analysis reveals a more complex picture:
- Supplier Price: $50.00 per valve
- Bulk Freight (Ocean): $2.50 per unit
- Import Tariff (10%): $5.00 per unit
- Customs Brokerage Fee: $0.75 per unit
- Warehouse Handling & Storage: $1.25 per unit
- Payment Processing Fee (2.9%): Calculated on the final sale price, adding another variable.
The initial $50.00 purchase price quickly becomes a $59.50 landed cost—before accounting for marketing, overhead, or profit. The pricing floor is not $50; it is nearly $60. Basing the price on the supplier cost alone would lead to unrealized margin erosion.
Without a meticulous breakdown of every expense, from tariffs to transaction fees, you are pricing in the dark. Establishing this precise cost floor is the first and most critical step in protecting your profitability and ensuring your pricing strategy is sustainable.
This requires diligence. Any miscalculation directly impacts your bottom line. The best practice is to create a detailed checklist of all possible costs and apply it to every product.
Gaining a Competitive Edge with Market Intelligence
Understanding your costs is critical for setting your price floor. However, the other, more dynamic part of the equation is understanding market demand and competitor activities.
Pricing in a vacuum based solely on internal numbers is a formula for commercial failure. It will lead to either pricing yourself out of the market or leaving significant revenue on the table. To succeed, you must move beyond occasional manual competitor checks and implement systematic market intelligence gathering.

Why Competitor Data Has a Direct Commercial Impact
Collecting market data is not an academic exercise; it directly impacts your bottom line. Accurate, real-time intelligence enables sharp, profitable decisions that provide a competitive advantage.
Here’s how this data translates into tangible business value:
- Spot Pricing Gaps: Immediately identify where prices are too high, costing sales, or too low, sacrificing margin.
- Identify Market Trends: Detect when a key competitor launches a major promotion or adjusts pricing on a product category, allowing for proactive responses.
- Enforce MAP/RRP Policies: For brands, tracking reseller pricing across numerous online marketplaces is essential for protecting brand integrity and maintaining channel partner relationships.
With global online retail sales projected to reach $7.4 trillion in 2025, a pricing strategy informed by real-time competitor data is non-negotiable. This shift means nearly one in four dollars will be spent online, making competitive price benchmarking essential for survival.
From Manual Checks to Automated Intelligence
For any growing business, transitioning from manual price tracking to automated intelligence is a necessity. A spreadsheet may suffice for a small number of products, but it quickly becomes a liability as you scale.
A pricing manager manually tracking 50 SKUs across 10 competitors is managing 500 data points. The process is not only tedious but also prone to human error, and the data becomes outdated almost immediately.
This is the point where spreadsheets are no longer a viable solution.
Pricing Data Source Comparison
The choice between manual and automated tracking directly impacts team efficiency and the quality of strategic decisions.
| Attribute | Manual Tracking (Spreadsheets) | Automated Monitoring (e.g., Market Edge) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | Prone to typos, copy-paste errors, and outdated information. | High accuracy with AI-powered product matching and validation. |
| Scalability | Extremely limited. Becomes unmanageable with more products or competitors. | Highly scalable; easily tracks thousands of SKUs across the entire web. |
| Timeliness | Static. Data is old the moment it's entered, missing daily price changes. | Real-time. Data is refreshed daily or on-demand for up-to-the-minute insights. |
| Team Focus | Staff spends hours on tedious, low-value data entry. | Team focuses on high-value strategic analysis and decision-making. |
| Violation Alerts | No automated alerts. Violations are found by chance, if at all. | Instant, automated alerts for MAP/MSRP violations with evidence. |
While manual methods may be suitable for small-scale operations, automated systems provide the robust, reliable intelligence required to compete effectively.
Automated price monitoring tools fundamentally change this process. These platforms use web crawlers and AI to match products and deliver clean, structured data directly to a dashboard. This allows pricing managers to focus on strategy instead of data collection.
For a deeper look at this technology, our guide on competitor price monitoring software provides a detailed breakdown.
Mini Use Case: A Manufacturer's MAP Enforcement
Consider a manufacturer of high-performance automotive parts with a strict MAP policy designed to protect its premium brand reputation. The company sells through a network of dozens of online resellers.
Without automation, MAP enforcement is ineffective. Manually checking each reseller's site for hundreds of SKUs is a full-time job that yields incomplete and outdated data. Violations can go unnoticed for weeks, leading to price erosion and frustrating compliant retail partners.
By implementing an automated system, the manufacturer gains a single dashboard showing every reseller's advertised price for every product, updated daily.
The system automatically flags any price below the MAP threshold, empowering the sales team to:
- Receive instant alerts when a MAP violation occurs.
- Generate clear proof of the violation, including timestamps and screenshots.
- Contact the non-compliant reseller immediately and professionally.
- Demonstrate to compliant partners a serious commitment to channel protection.
A platform like Market Edge automates the entire data collection and violation detection process, enabling the manufacturer to enforce its policies effectively. This protects brand value and maintains a healthy distribution network by shifting the team's focus from manual tasks to strategic enforcement.
Using Advanced Pricing Models to Maximize Revenue
Once you have established your costs and analyzed the competitive landscape, it is time to move beyond basic models. Simple cost-plus or competitor-matching strategies are safe but often leave revenue on the table.
Sophisticated models shift the focus from a product's cost to its worth to the customer. This is the difference between pricing for survival and pricing for strategic growth. While it requires deeper insights, it unlocks significantly higher profit potential.
Tying Price Directly to Customer Value
The first step toward advanced pricing is adopting a value-based model. This approach anchors your price to the tangible value your product delivers, rather than your costs or competitor prices. The central question becomes, "How much is this solution worth to our customer's business?"
Implementing this model requires quantifying that value through structured research.
- Interview your customers. Engage directly with your ideal B2B clients. Ask them what problems your product solves, how much time it saves, or what new revenue it helps them generate.
- Translate features into financial benefits. If your industrial component lasts 25% longer than a competitor's, that represents a direct reduction in downtime and maintenance costs for your client. This is quantifiable value.
- Segment your buyers. Different customers derive different levels of value from the same product. An enterprise may value a software feature for its scalability, while a small business values its ease of use. Your pricing should reflect these differences.
For example, a project management software company doesn't base its subscription fee on server costs. It prices based on the documented hours of administrative work the software saves a team each month, which translates directly into thousands of dollars in labor savings for its B2B clients.
Leveraging Real-Time Data with Dynamic Pricing
Another powerful strategy is dynamic pricing, which involves adjusting prices in real-time based on market conditions. This is not about random price changes but a disciplined, data-driven approach that responds to shifts in supply, demand, competitor actions, or even the time of day.
This strategy is particularly effective in ecommerce, where price changes can be implemented instantly. Consider a B2B supplier of seasonal construction materials.
With a dynamic pricing model, they can automatically increase prices during the peak spring building season when demand is high, maximizing revenue. As demand decreases in the fall, prices can be strategically lowered to clear inventory and avoid storage costs.
This agility is impossible without a constant stream of reliable data. You need to know the moment a key competitor goes out of stock, creating an opportunity to capture demand at a higher margin. This is where automated monitoring becomes a core operational tool. For more on this topic, see our deep dive into price optimization software.
The pressure to implement such strategies is growing. The 2025 Consumer Products Outlook notes that executives are moving away from broad price hikes due to high price sensitivity among customers, who will quickly trade down. A tiny 0.8% global shift to lower-priced products can eliminate billions in revenue for mid-tier brands. This highlights the need for a strategy anchored in perceived value and competitive positioning, not just internal costs.
Advanced models are not mutually exclusive. A value-based framework can set your baseline RRP, while dynamic pricing can be layered on to react to market shifts on specific channels. The common requirement for both is accurate, up-to-the-minute data.
This is where automated price monitoring tools like Market Edge come in, providing the continuous market intelligence needed to power these more profitable and responsive pricing strategies.
Putting Your Pricing Strategy into Action
Analysis is meaningless if your pricing strategy remains a theoretical exercise. The true test is operationalizing your models into practical rules within your ERP or ecommerce platform. This is where strategy translates into daily revenue generation.
Effective execution requires establishing clear guardrails for all transactions. This includes setting rules for promotions, defining tiers for volume discounts, and building distinct pricing structures for different channels, such as direct-to-consumer versus wholesale partners. Without these rules, pricing becomes inconsistent, leading to channel conflict and margin erosion.

Staying Agile When the Market Gets Volatile
Pricing rules cannot be static. Today's markets are volatile, and your pricing must be agile enough to absorb external shocks like sudden import tariffs, supply chain disruptions, or currency fluctuations. A failure to adapt quickly can have severe commercial consequences.
Consider a scenario where a 15% tariff is imposed on key electronic components you import. A rigid pricing framework forces a difficult choice: absorb the cost and sacrifice 15% of your margin, or begin the slow, error-prone process of manually repricing thousands of SKUs.
An agile strategy enables a swift and precise reaction:
- Immediately update the landed cost formula in your system.
- Recalculate the pricing floor for all affected products.
- Implement a temporary surcharge or adjust list prices across specific channels to protect profitability.
This responsiveness prevents catastrophic margin loss and maintains business stability during turbulent market conditions.
How Automation Makes Agile Pricing Possible
Agility is powered by real-time data. Looking ahead, factors like potential tariffs and supply chain issues will continue to influence pricing. As noted in analyses of pricing trends and their impact, persistent disruptions and rising material costs are putting immense pressure on manufacturers, with 64% reporting increased demands from customers during negotiations. This necessitates robust scenario planning and competitive intelligence.
Manually tracking market shifts, competitor actions, and cost changes across a large product catalog is not sustainable. It is too slow, resource-intensive, and guarantees you will always be reacting to past events.
This is where automated price monitoring tools like Market Edge prove their value. By providing a continuous stream of clean, real-time market data, these platforms empower you to react to market events instantly. Instead of waiting for a quarterly report, you can adjust your pricing rules and strategies based on current conditions, protecting margins and maintaining a competitive edge.
Your Actionable Product Pricing Checklist
Effective product pricing is an ongoing business function, not a one-time project. This checklist distills the process into actionable steps for pricing managers and business leaders. It is designed to ensure all critical components are consistently addressed, from initial cost analysis to ongoing market monitoring.
Laying the Groundwork
The foundation of any pricing strategy is accurate data. Compromising on this step will undermine the entire structure.
-
Calculate Your True Landed Cost: Go beyond the supplier invoice. Include COGS, inbound freight, tariffs, customs fees, warehousing, and payment processing fees. This total represents your absolute price floor.
-
Set Up Competitor Monitoring: Identify your top three to five competitors and begin systematically tracking their pricing, promotions, and stock levels across all sales channels. Manual tracking is not scalable; a systematic approach is required.
-
Define and Quantify Your Value: What makes your product superior? Is it more durable? Does it save the customer time? Is your warranty or support a key differentiator? Quantify this value where possible to justify your price point.
Putting Your Strategy into Action
With a solid data foundation, you can build and implement your pricing model.
A pricing strategy is only as effective as its execution. This means translating your analysis into clear, enforceable rules within your sales and ecommerce platforms, ensuring consistency across every transaction.
-
Choose Your Core Pricing Model: Select the model that aligns with your goals. For guaranteed profit, cost-plus is simple. To stay aligned with the market, use competitive pricing. To capture maximum margin with a superior product, use value-based pricing.
-
Establish Your Rules of Engagement: Define your commercial guardrails. Set tiers for volume discounts, establish promotional guidelines, and differentiate pricing between direct and partner channels. This prevents margin erosion and maintains channel harmony.
-
Schedule Regular Price Reviews: The market is constantly changing. Schedule a recurring meeting—quarterly or semi-annually—to review your pricing against sales data, competitor actions, and market trends.
This is where automated price monitoring tools like Market Edge deliver significant value by automating the market tracking process, freeing your team to focus on strategy.
Your Pricing Questions, Answered
Several common questions arise when implementing a pricing strategy. Here are answers for founders, brand managers, and sales leaders.
What's the Real Difference Between Margin and Markup?
Confusing these two terms can lead to significant underpricing. They represent two different financial calculations.
- Markup is the percentage added to your cost to determine the selling price. It answers the question, "By what percentage did I increase the cost?"
- Margin is the percentage of the final selling price that represents profit. It answers the question, "What percentage of the final price is profit?"
For example, a product costs $50 and sells for $100. The markup is 100% (a $50 increase on a $50 cost). However, the gross profit margin is 50% (the $50 profit is half of the $100 selling price).
Mistaking one for the other will directly impact your profitability.
How Often Should I Actually Revisit My Prices?
Pricing is not a static decision. A formal, comprehensive pricing review should occur at least quarterly or semi-annually.
However, certain events require an immediate response:
- Significant cost changes: A new tariff, a rise in shipping rates, or a spike in raw material costs necessitates an immediate re-evaluation.
- Major competitor actions: A rival launching a significant, long-term promotion or a widespread price reduction requires a strategic response.
- Sudden shifts in demand: A rapid increase or decrease in sales for a product may indicate a pricing misalignment.
Your ability to react quickly to these triggers is what separates the businesses that thrive from those that just survive. This is where continuous price monitoring comes in—it gives you the data to be agile instead of just reacting months later.
What's the Best Way to Actually Enforce MAP or RRP?
Enforcing a MAP/RRP policy with manual spot-checks is ineffective. It is slow, inconsistent, and lacks the concrete evidence needed for enforcement.
The only effective method is automated ecommerce and marketplace monitoring. An automated system works 24/7 to track reseller prices, capture time-stamped screenshots as evidence, and send alerts the moment a price drops below the established threshold.
This provides your team with the necessary documentation to address violations quickly and consistently, protecting your brand integrity and ensuring a level playing field for all retail partners. This is precisely what automated tools like Market Edge are designed to do.
Ready to stop guessing and start pricing with precision? Market Edge delivers the real-time competitor and market intelligence you need to protect your margins, enforce your pricing policies, and make smarter decisions. See how it works.